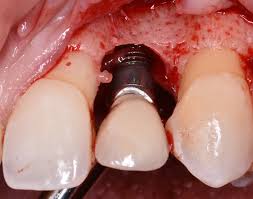
Article
Prosthetic Design Factors That Prevent Peri-Implant Bone Loss
You placed the implant perfectly. Osseointegration was flawless. But three years later, there is 3mm of bone loss around the fixture.
What went wrong? More than often, it is not the surgery but it is the restoration.
The 2024 AO/AAP Consensus analyzed multiple studies and revealed exactly which prosthetic design choices protect bone and which cause bone loss. These are decisions YOU can control at the restorative phase.
Design Factors That Matter
Here is the list of factors that matter for the prosthesis -
1. Individual Crowns Over Splinted Restorations
Non-splinted implants showed significantly less marginal bone loss than splinted implants.
Why it matters? Splinting makes oral hygiene maintenance harder and may lead to the transmission of forces differently.
Clinical action? Opt for an individual tooth-replacement restoration unless there is a specific reason to splint.
2. Platform Switching Reduces Bone Loss
Platform-switched abutments showed reduced bone loss compared to platform-matched abutments.
What it means? Platform switching uses an abutment narrower than the implant, let’s say a 4mm abutment on a 5mm implant. This creates a horizontal offset that moves the implant-abutment connection inward and away from the surrounding bone.
Since bacteria colonize this connection area, moving it away from the bone can reduce inflammatory bone loss.
Clinical action? When selecting implant systems, choose platform-switched connections. Most modern systems, like Straumann, Nobel Biocare, and Zimmer, offer this as standard. It is not complicated or an extra step; just order the appropriately sized abutment for your implant platform.
3. Abutment Height Matters
Abutments that are ≥2mm tall resulted in significantly less bone loss than abutments that were less than 2mm.
Why it matters? Taller abutments generally provide more space for healthy soft tissue attachment and therefore, help maintain biological width.
Clinical action? Use abutments that are at least 2mm in height. Don't compromise with short abutments to save vertical space.
4. Leave the Abutment Alone
Leaving abutment in place resulted in significantly less bone loss than repeated removal and reconnection.
Why it matters? Every disconnection disrupts the soft tissue seal and may be a pathway to introduce bacteria.
Clinical action? Minimize abutment changes during restoration. Plan treatment in a way that you don't have to do too much removal. Once placed, leave it alone.
5. Emergence Profile Design
Emergence angles <30° are associated with lower peri-implantitis risk. Concave or straight emergence profiles can reduce the risk compared to convex profiles.
Why it matters? Bulky, overcontoured restorations can create plaque traps that make oral care at home harder.
Clinical action: Design restorations with gentle emergence angles. Avoid using bulbous crowns and keep profiles concave or straight, not convex.
What Surprisingly Doesn't Matter?
These are things that were supposedly a deal breaker but are not -
Screw-Retained vs. Cement-Retained
No significant difference in bone loss was found.
However, excess subgingival cement is a problem, but that is execution, and not an inherent flaw. While cementing focus on complete excess removal. Due to factors like these, the consensus prefers screw retention.
Crown-to-Implant Ratio
No significant impact on bone loss was found.
Clinical takeaway: High crown-to-implant ratios don't doom the case. Rather, focus on occlusion and hygiene access.
Your Evidence-Based Prosthetic Checklist
✅ Individual crowns over splinted when possible
✅ Platform-switched connections
✅ Abutments ≥2mm tall
✅ Minimize abutment removal after initial placement
✅ Emergence angle <30°
✅ Concave or straight emergence profile
✅ Complete cement removal if using cement retention
Final Takeaway
The 2024 AO/AAP Consensus gives you a design blueprint which is backed by meta-analysis. Some factors matter a lot while others don't matter as much as we thought.
These simple prosthetic choices can either give you 20 years of stable bone and progressive peri-implantitis.Make sure you choose the right ones.
References
- Wang HL, Avila-Ortiz G, Monje, Rosen PS et al; AO/AAP Consensus Participants. AO/AAP consensus on prevention and management of peri-implant diseases and conditions: Summary report. J Periodontol. 2025;96(6):519-541.
- Lin GH, Lee E, Barootchi S, Kan JY, Rosen PS. The influence of prosthetic designs on peri-implant bone loss: An AO/AAP systematic review and meta-analysis. J Periodontol. 2025. doi:10.1002/JPER.24-0144
- Fiorellini JP, Mojaver S, Sarmiento H, Aghaloo T. Clinical translation of the 2024 AO/AAP Consensus on prevention and management of peri-implant diseases and conditions. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2025;45(4):1-23.
Related Contents
Article
Treatment Algorithms for Peri-Implant Mucositis and Peri-Implantitis
You can prevent most peri-implant disease. But once it develops, treatment becomes less predictable....
Article
Implant Surface Decontamination: What Actually Works
Treating peri-implantitis starts with one critical step, which is decontaminating the implant surfac...

Article
Growth & Facial Asymmetry: When to Worry
Only a few dentists can notice it and realize the asymmetry can signal an underlying skeletal imbala...

Article
Orthodontic Red Flags Every Dentist Should Recognize: Functional Habits and Airway Cues
Some malocclusions cases stall for reasons you can’t see on a scan, as not...
Article
Tooth Eruption & Space Management: What Orthodontists Should Watch For
Tooth eruption may not alwaxfys fit the predictable biological timeline. A delayed or ecto...
Article
Communication & Referral Timing: Getting It Right
You have identified a problem, maybe a severe Class III malocclusion in a 9-year-old, or it is an im...
Article
Rotary File Fatigue – How to Prevent Separation?
File breakage in maxillary molars is not a rare sight, but definitely no less than a nightmare. But...
Article
Modern Irrigation Activation: Ultrasonic vs Sonic vs Laser
After shaping the canal, irrigation determines whether bacteria will stay or be washed away. ...